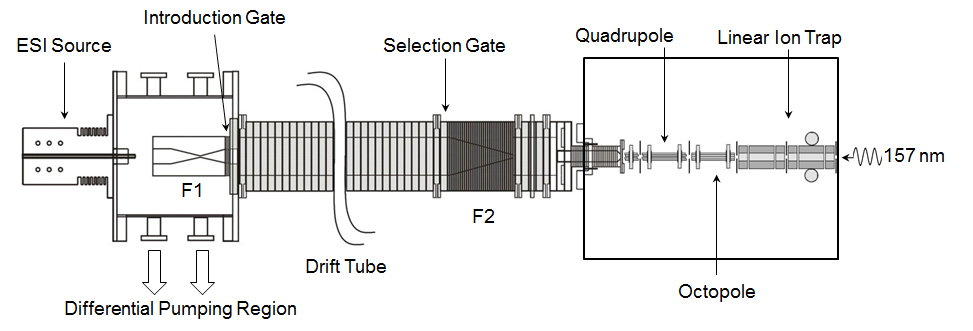
Figure 1 shows a schematic of the new IMS-MS instrument. The front half, up to and including the second funnel (F2 in Figure 1), is similar to instruments described previously. Briefly, ions from an electrospray ionization (ESI) source are continuously focused through and collected in an hour-glass ion funnel (F1). Periodically the ions are pulsed into the linear drift region that is ~1 meter long and filled with ~3 Torr of a buffer gas mixture (He and Air). Ions traverse the drift region under the influence of a uniform electric field where they separate according to differences in their mobilities through the buffer gas. Ions are then selected by these mobilities using an ion selection gate and enter a second ion funnel (F2) where they are radially focused to the center axis of the drift tube. Upon exiting the F2 region, ions traverse a short (~5 cm) drift interface region prior to exiting the drift tube through a conductance limiting (0.20 cm) aperture. Here the ions enter the LTQ Velos instrument (Thermo Electron, San Jose, CA, USA) where they are directed by radio frequency (rf) guides into the higher-pressure linear ion trap. They are subsequently passed to the lower-pressure linear ion trap where they are stored, mass analyzed, and periodically subjected to ion dissociation steps (VUV PD and/or CID).